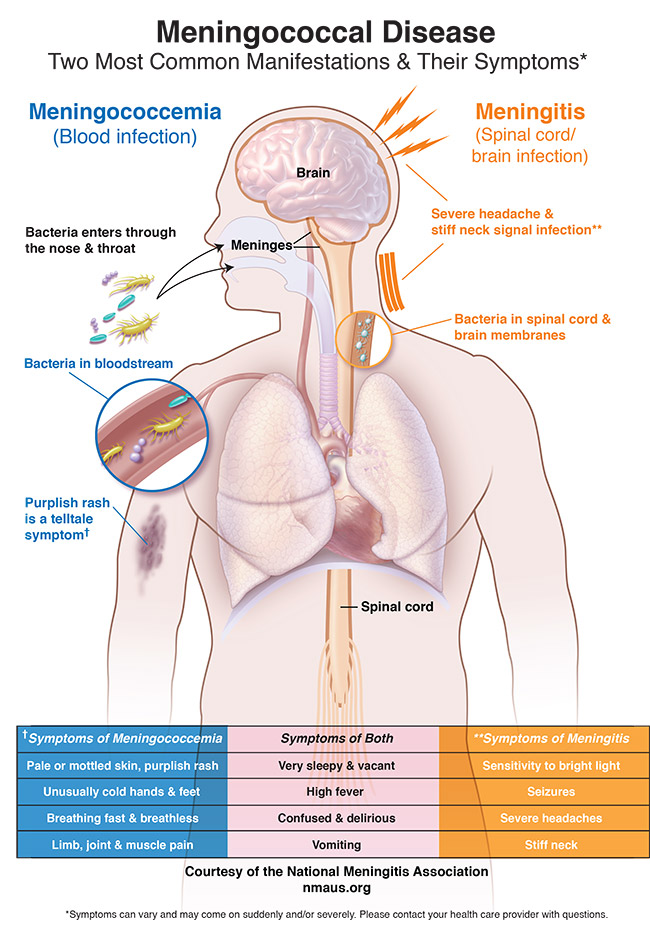
Your baby may be hard to comfort especially when theyre being held. Symptoms of pneumococcal meningitis an infection of the lining of the brain and spinal cord include.
 Pneumococcal Meningitis Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Pneumococcal Meningitis Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Encephalitis can be characterized by fever seizures change in.

Pneumococcal meningitis symptoms. Bacterial meningitis commonly presents with symptoms such as headache impaired consciousness neck stiffness and fever. Overall its estimated up to 1 in every 10 cases of bacterial meningitis is fatal. C0025295 A rare infectious disease of the nervous system caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae which is commonly part of the bacterial flora colonizing the nasopharyngeal mucosa.
Pneumococcal meningitis is an infection of the tissue covering the brain and spinal cord. Bulging fontanelles in infants. A high temperature fever of 38C 1004F aches and pains.
For the elderly they may include confusion low alertness and the former listed symptoms to a lesser degree. Unusual posture with the head and neck arched backwards opisthotonos Pneumococcal meningitis is an important cause of fever in infants. The symptoms of meningitis can come on very rapidly.
Loss of limbs amputation of affected limbs is sometimes necessary. Poor feeding or irritability in children. An estimated 2000 cases of pneumococcal meningitis occur each year.
Meningitis is an acute inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord known collectively as the meninges. Signs and symptoms may include. Other symptoms in a baby may include.
Ad If you believe the official pronouncements of top governmental health agencies like the. Recurrent seizures epilepsy co-ordination movement and balance problems. Types of pneumococcal infection.
In babies meningitis may cause poor eating and drinking low alertness and vomiting. The hallmark signs of meningitis include some or all of the following. Less common early symptoms include shivering diarrhoea abdominal pain and distention coryza and other ear nose and throat symptoms.
The disease is clinically characterized by typical symptoms of acute leptomeningitis like fever headache neck. The symptoms of pneumococcal meningitis usually come on rapidly. Ad If you believe the official pronouncements of top governmental health agencies like the.
General features of meningitis include a nonÂ-blanching rash that can appear anywhere on the body altered mental state shock unconsciousness and toxic or. The symptoms of a pneumococcal infection can vary depending on the type of infection you have. Symptoms of pneumococcal meningitis include.
Pneumococcal meningitis Concept Id. It can be life-threatening and a person who develops pneumococcal meningitis will usually need to spend time in the hospital. Pneumococcal meningitis symptoms start suddenly usually within 3 days of infection with the bacteria.
The most common symptoms are fever headache and neck stiffness. In some cases the symptoms may develop sooner or later than that. In a nationwide study in the Netherlands comprising 696 cases of bacterial meningitis at least two of these symptoms were present in 95 of cases 1.
Other symptoms that can occur with this disease. Some patients with pneumococcal meningitis also have pneumonia. Symptoms include stiff neck fever headache confusion and photophobia.
An infected person may develop the following. The clinical symptoms cerebrospinal fluid CSF profile and neurologic complications are similar to other forms of purulent bacterial meningitis. Find out more about the complications of meningitis.
Sudden fever severe headache nausea or vomiting double vision drowsiness sensitivity to bright light and a stiff neck. Photophobia eyes being more sensitive to light Confusion. Other symptoms include confusion or altered consciousness vomiting and an inability to tolerate light or loud noises.
CDC and FDA all the vaccines in the present day schedule are a priori safe and effective. CDC and FDA all the vaccines in the present day schedule are a priori safe and effective.

/meningitis-diagnosis-20-5ae0c022ae9ab8003740634d.png)

/meningitis-symptoms-5af1aa991f4e1300375f6d48.png)