Treatment for nontuberculous mycobacteria will depend on the specific bacteria causing your infection. Nontuberculous mycobacteria NTM are mycobacteria other than M.
 Antibiotics Free Full Text Efficacy And Mechanisms Of Flavonoids Against The Emerging Opportunistic Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Html
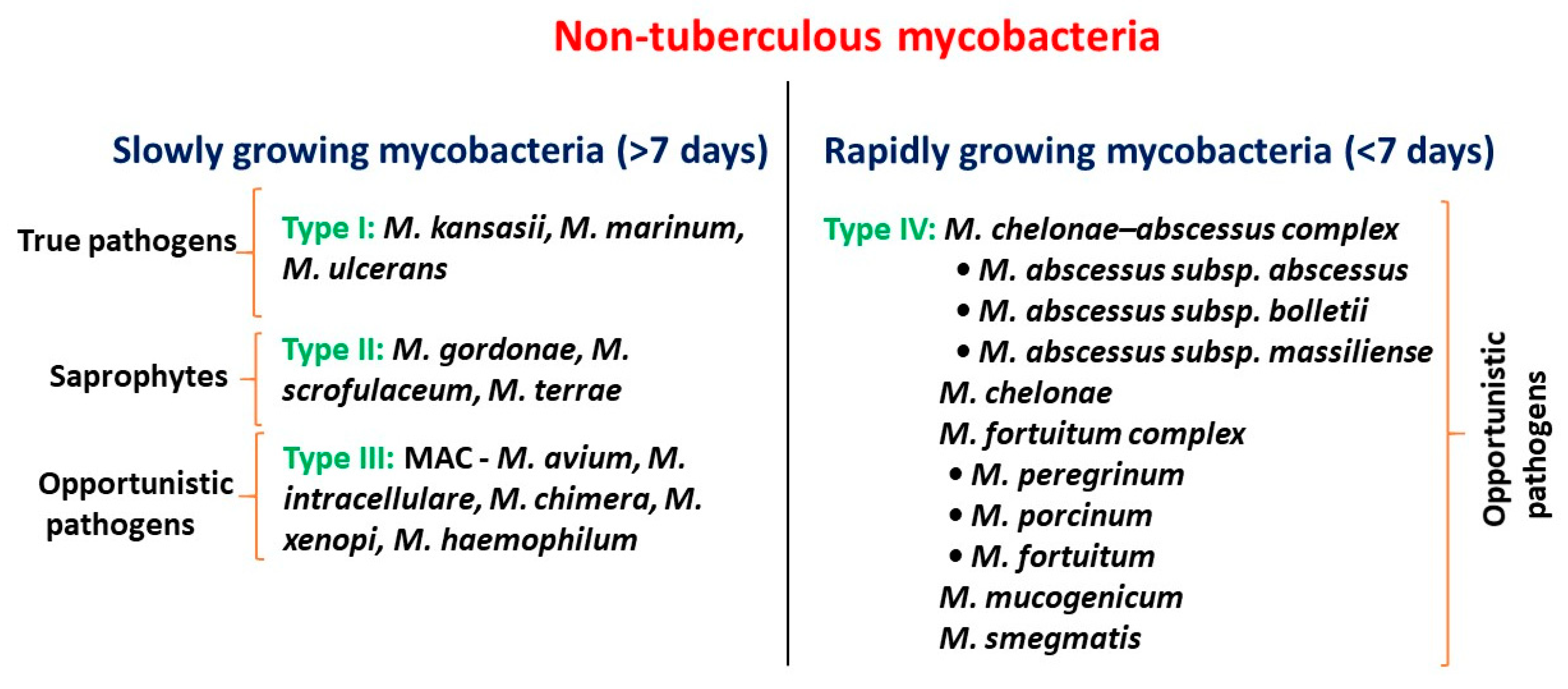
Antibiotics Free Full Text Efficacy And Mechanisms Of Flavonoids Against The Emerging Opportunistic Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Html
Although NTM are not obligate pathogens they share with M.

Non tuberculosis mycobacterium treatment. Overall both by imaging and symptoms NTM lung disease resembles tuberculosis however the symptoms are less severe. A few of the NTM infections such as those caused by Mycobacteria ulcerans are best treated by surgical removal of damaged skin debridement to prevent further spread of the infection. Many patients develop persistent chronic infection despite treatment while others succumb to the disease 5 67.
Take your medication as prescribed and do your chest physiotherapy exercises regularly if you have. The treatment regimens recommended vary greatly depending on the species. The duration of the treatment may be for at least a year.
Have a flu jab each year eat a healthy balanced diet and if you smoke stop. Antimycobacterial therapy may also hasten recovery and prevent the uncommon development of chronic disease. In cases where the infection is localized such as an infected lymph node the infected tissue may be surgically removed.
Side effects of antibiotics are numerous and regimes are difficult to tolerate. Treatment is at high cost USD 14730 for MAC infection and USD 47240 for MABS infection 67. Although anyone can get an NTM infection NTM are opportunistic pathogens.
Tuberculosis complex MBTC the features of hardiness hydrophobicity aerosolization and intracellular pathogenicity. Treatment may be difficult because NTM bacteria may be resistant to many common types of antibiotics. The prognosis is good and a prompt resolution of symptoms is expected following treatment.
Our Approach to Nontuberculous Mycobacteria NTM infections can cause symptoms seen in other lung conditions making diagnosis a challenge. Due to the length of time required to kill all the NTM bacteria treatment may last a full year or two. In some cases the NTM infection becomes chronic long term and requires continuous treatment.
Nontuberculous mycobacterial NTM infections of the lungs often occur in the context of preexisting lung disease especially chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD bronchiectasis pneumoconiosis cystic fibrosis and previous tuberculosis 1-4. Nontuberculous mycobacterial lung infections are rare and may require prolonged antibiotic treatment sometimes for two years or more. However the treatment of drug-resistant TB requires the additional newer class of antibiotics in combination with or without the first and second-line drugs.
The best way to help your lungs fight off an NTM infection is to keep active and to look after yourself. There may be significant side effects due to chronic use of antibiotics and hence the treating physicians carefully monitor patients under treatment for Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Infections. NTM are also referred to as atypical mycobacteria mycobacteria other than tuberculosis MOTT or environmental mycobacteria.
Even though the lung is the most common organ involved NTM can cause disease in other organs of the body. Recent Findings Emerging pathogens includeMycobacterium chimaera and drug-resistant subspecies ofMycobacterium abscessus. For some patients the same drugs used.
Leprae the cause of leprosy. In general drug-sensitive TB is effectively treated with a standard multi-drug regimen containing well-defined first- and second-line antibiotics. Almost all of the Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Infections are treated with strong antibiotics.
Most of the nontuberculous mycobacteria are naturally resistant to common antibiotics. Unlike other NTB diseases short courses of antimicrobial drugs 3 to 6 months are usually effective. Some of medications used to treat NTM happen to treat tuberculosis TB as well.
As a result the clinical manifestations of NTM lung disease are often similar. Non-tuberculous mycobacteria NTM are ubiquitous environmental acid-fast bacilli AFB. If you take all your NTM medication for the full treatment periods you should be cured of your infection.
UCSF pulmonologists are experts at detecting and treating these infections and tailor therapy to the species of bacteria causing each patients illness. Tuberculosis the cause of tuberculosis and M. Purpose of Review This review describes recent trends in the epidemiology of nontuberculous mycobacteria NTM emerging pathogens new insights into NTM pathogenesis and advances in diagnosis and treatment.