This type involves the coronal sutures that run from each ear to the top of the babys skull. Unilateral Coronal Synostosis.
Is This Weird Head Ridge Concerning Babycenter
2 following a zigzag sinusoidal pattern in order to create a stealth incision which would be cosmetically acceptable as it would heal with less scarring due to a repeated change in the direction of force vectors.
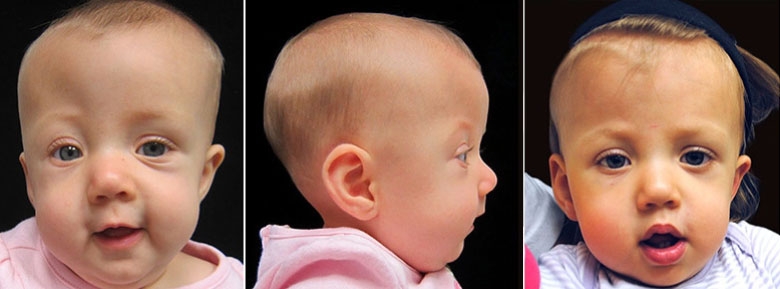
Coronal suture ridge. Unicoronal craniosynostosis is a type of non-syndromic craniosynostosis and occurs when one of the two coronal sutures fuses before birth. It accounts for 20 to 30 percent of cases. The two sides of the forehead are marked by the temporal ridge a bone feature that links the supraorbital ridge to the coronal suture line and beyond.
Unilateral craniosynostosis is typically characterized by the harlequin eye almond shaped and a flattened forehead. Figure 6 Superior view from a 3D CT scan of the skull of a 6-month-old infant showing scaphocephaly and fusion of the sagittal suture with a midline ridge. It causes the forehead to appear flat on one side and bulging on the other.
The borders where these plates intersect are called sutures or suture lines. This is a term sometimes used to describe the premature closure of the coronal suture plus any other suture like the lambdoid suture citation needed Pansynostosis edit The word pansynostosis is also Greek derived and can be translated as all one bone indicating that all of the sutures are closed. For example a fused coronal suture may cause a.
The skull of an infant or young child is made up of bony plates that allow for growth of the skull. This page from Great Ormond Street Hospital GOSH explains the causes symptoms and treatment of unicoronal craniosynostosis and where to get helpThe coronal sutures run from the front fontanelle down to the. Niosynostosis might reveal a ridge over a suture or lack of movement along a suture when al-ternating sides are gently pressedOverriding of sutures from the normal molding process.
A raised ridge develops along the fused sutures in the skull Other problems happen depending on which of the sutures grow together. There is a coronal suture on both sides of the skull. This type happens when one or both of the sutures that connect the top of the head to the ears join too early.
One or both sutures can become fused and this results in a flat forehead and a difference in the appearance of the eyes with one being more open than the other. These are the coronal sutures. This makes the bony plates overlap at the sutures and creates a small ridge.
The borders where these plates intersect are called sutures or suture lines. When both coronal sutures are affected a ridge can be felt on both sides of the head running from the top of the skull down the sides in front of the ears. The skull of an infant or young child is made up of bony plates that allow for growth of the skull.
One of the coronal sutures the seams that runs from the ear to the soft spot on top of the babys head Cause and occurrence. The AF coronal and lambdoid sutures are all patent. It produces a boat-shaped head that is longer than it is wide and is associated with frontal bossing and a palpable ridge along the closed suture.
Bilateral coronal synostosis brachycephaly is characterized by a shortened skull in the. In an infant only a few minutes old the pressure from delivery compresses the head. Such an incision is also less noticeable later in life as the hair will not part along a zig zag line as easily as it will along a straight incision line particularly.
This makes the bony plates overlap at the sutures and creates a small ridge. Depending how early this is discovered the forehead will appear flat and under-projected. The coronal suture runs from the top of the skull down the sides towards the corner of the eye.
The cause is unknown but can be related to underlying associated genetic malformation in upwards of 20 to 30 of cases. The bilateral coronal incision was marked Fig. In an infant only a few minutes old the pressure from delivery compresses the head.