The live virus used in the vaccine can rarely shed in the stool and can rarely spread to others within a community. Killed inactivated vaccines are made from a protein or other small pieces taken from a virus or bacteria.
 Module 2 Live Attenuated Vaccines Lav Who Vaccine Safety Basics
Module 2 Live Attenuated Vaccines Lav Who Vaccine Safety Basics
The live virus also has stringent requirements for transport and storage which are a problem in some hot or remote areas.
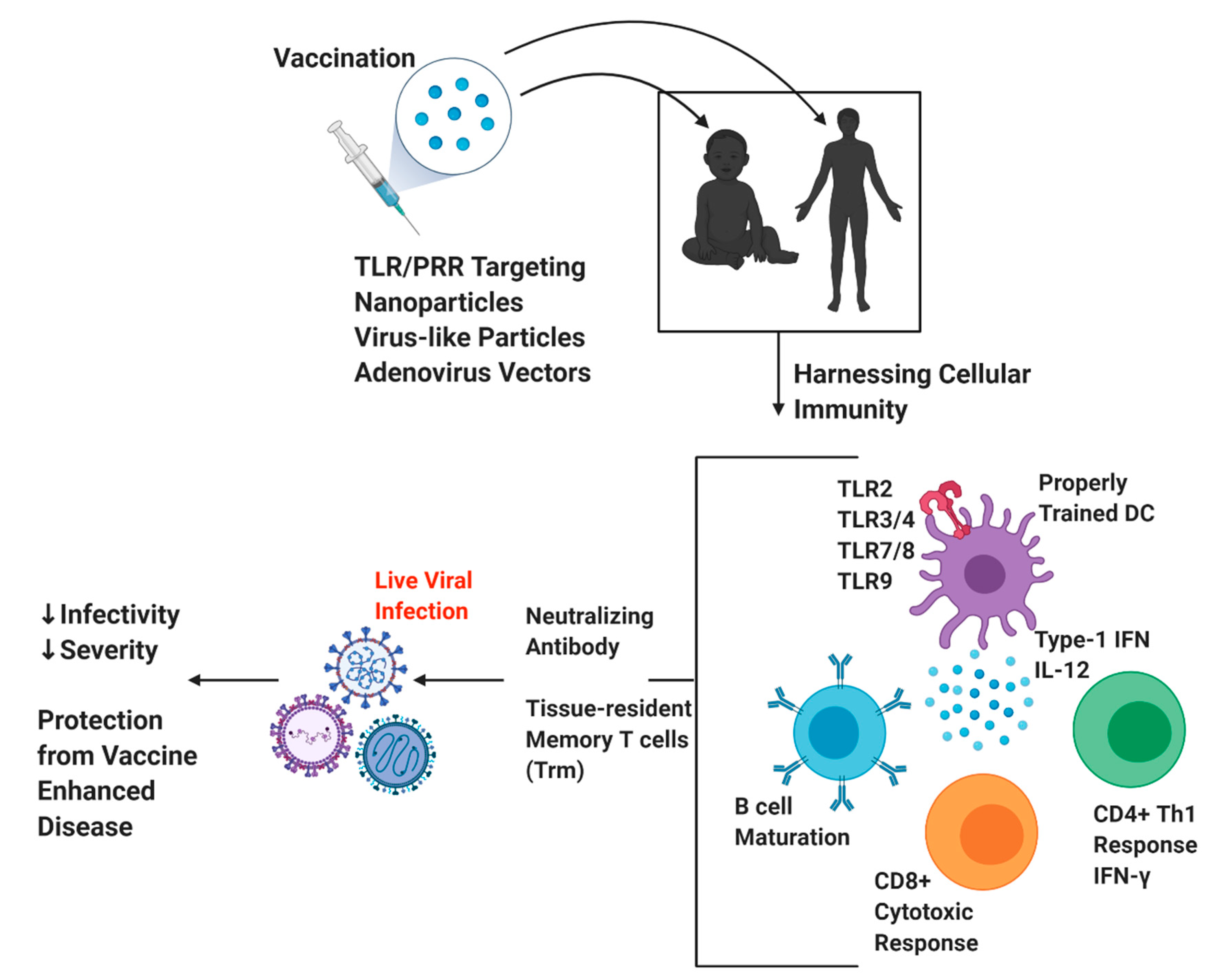
Live virus vaccines. Both mRNA and viral vector COVID-19 vaccines deliver instructions genetic material to our cells to start building protection against the virus that causes COVID-19. Live vaccines contain a live vaccine virus that must replicate in the body in order to stimulate immunity. Instead they use an adenovirus vector which is.
Anything that interferes with that replication might impact the immune response. Examples include vaccines against the measles mumps and rubella. Examples include vaccines against the measles mumps and rubella.
The whooping cough pertussis vaccine is an example. One is a live attenuated vaccine which delivers a weakened but active virus into the body while a killed inactivated vaccine delivers a shot of dead. Live virus vaccines use the weakened attenuated form of the virus.
The chickenpox vaccine and polio vaccine work the same way too. As with other live-virus vaccines immunity initiated by OPV is. There are currently two types of COVID-19 vaccines that have been authorized and recommended for use in the United States.
Because theyre similar to infectious viruses developers take. In this type of vaccine genetic material from the COVID-19 virus is inserted into a different kind of weakened live virus such as an adenovirus. Viral vaccines contain either inactivated viruses or attenuated alive but not capable of causing disease viruses.
Inactivated or killed viral vaccines contain viruses which have lost their ability to replicate and in order for it to bring about a response it. The JanssenJohnson Johnson COVID-19 vaccine is a vector vaccine. The chickenpox vaccine and polio vaccine work the same way too.
Live attenuated virus vaccines Live attenuated virus LAV vaccines have been a reliable means of inducing effective long-term immunity against various specific viral pathogens such as polio and. The measles mumps and rubella MMR vaccine and the varicella chickenpox vaccine are examples. The currently authorized Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine is not a live vaccine.
Steve Feagins Hamilton County Public Health medical director explained that the vaccines dont use live viruses. Viral vector vaccines combine many of the positive qualities of DNA vaccines with those of live attenuated vaccines. Live-attenuated vaccines differ from traditional inactivated vaccines where the pathogen is killed and as the name suggests the pathogen typically a virus remains active in live vaccines.
There is not a live component to. The 4-day grace period does not. Because theyre similar to infectious viruses developers take.
Both the Pfizer and Moderna vaccine are mRNA vaccines. Vaccination with the live but attenuated organism generates an immune response that protects the vaccinated person against severe disease or even infection. What are Viral vaccines.
1 Like DNA vaccines viral vector vaccines carry DNA into a host cell for production of antigenic proteins that can be tailored to stimulate a range of immune responses including antibody T helper cell CD4 T cell and cytotoxic T lymphocyte CTL CD8 T cell. Live attenuated vaccines are created by weakening infectious organisms that can still replicate and induce protective immune responses without causing disease in the host. Live vaccines can be given on the same day.
Messenger RNA mRNA vaccines and a viral vector vaccine.