Ad Experts in Trimix and we are standing by to help you now. Antibody-Dependent Enhancement Immune enhancement is believed to play a role in the pathogenesis of dengue hemorrhagic fever in patients with nonneutralizing antibodies from a previous dengue infection who are infected with a new dengue serotype.
 A Perspective On Potential Antibody Dependent Enhancement Of Sars Cov 2 Nature
A Perspective On Potential Antibody Dependent Enhancement Of Sars Cov 2 Nature
This effect was first identified in dengue virus and has since also been described for coronavirus.
Antibody dependent enhancement definition. Mediation by Fc receptors RECEPTORS FC or by complement receptors RECEPTORS COMPLEMENT. These antibodies could then enhance viral entry into. Mediation by Fc receptors RECEPTORS FC or by complement receptors RECEPTORS COMPLEMENT.
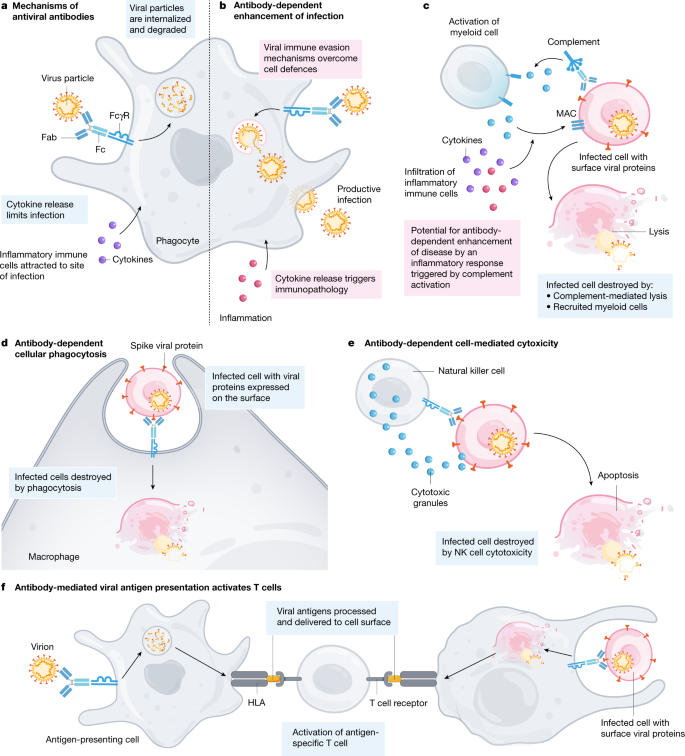
Antibody-dependent enhancement ADE exists in several kinds of virus. Early during an infection these responses are non-specific meaning that although they are directed at the pathogen they. The ADE of virus infection is a phenomenon in which virus-specific antibodies enhance the entry of virus and in some cases the replication of virus into monocytesmacrophages and granulocytic cells through interaction with Fc andor complement receptors.
Mediation by Fc receptors RECEPTORS FC or by complement receptors RECEPTORS COMPLEMENT. Antibody-Dependent Enhancement ADE appears to be a damaging inflammatory reaction of ones own antibodies against ones own tissues or cells again provoked by antibodies binding to ones tissues or by immune complexes being deposited. There are at least two mechanisms known to account for this.
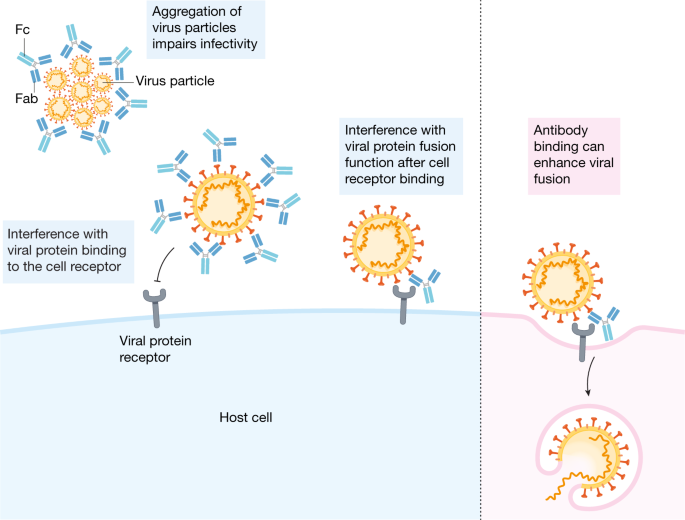
Antibody Dependent Enhancement ADE was the primary reason that the years of effort to develop a vaccine for SARS-cov-1 responsible for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in 2002-4 had to be abandoned. Enhancement of viral infectivity caused by non-neutralizing antibodies. Antibody-dependent enhancement ADE is an intriguing mechanism by which certain antibodies actually enhance viral replication by promoting entry of the pathogen into immune cells eg macrophages resulting in worsening of the infection1-4 Although these antibodies are pathogen-specific they are commonly not neutralizing or only.
Ad Experts in Trimix and we are standing by to help you now. This activity is known as antibody-dependent enhancement ADE of virus infection. Although animal test subjects developed antibodies they were made very sick when re-exposed to SARS-cov-1.
Data from the study of SARS-CoV and other respiratory viruses suggest that anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies could exacerbate COVID-19 through antibody-dependent enhancement ADE. Vaccine developers and the FDA are all looking carefully for any evidence of ADE and will continue to do so. Antibody-dependent enhancement or ADE is not a concern with the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines and will not likely be a concern with the other vaccines that will be approved.
Antibody-Dependent Enhancement Enhancement of viral infectivity caused by non-neutralizing antibodies. Previous respiratory syncytial virus and dengue virus vaccine studies revealed human clinical safety risks related to ADE resulting in failed vaccine trials. There are at least two mechanisms known to account for this.
Enhancement of viral infectivity caused by non-neutralizing antibodies. Antibody-dependent enhancement of influenza disease promoted by increase in hemagglutinin stem flexibility and virus fusion kinetics. Antibody-dependent Enhancement ADE and Vaccines Immune responses to pathogens involve many cells and proteins of the immune system.
Either the virus is complexed with antiviral IMMUNOGLOBULIN G and binds to Fc receptors or. There are at least two mechanisms known to account for this. It has a negative influence on antibody therapy for viral infection.
The process is called antibody-dependent enhancement ADE where a vaccine generates antibodies and binds the virus but does not neutralize it.