The most common causes of inner ear damage especially in children are recurring ear infections. Fluid and pus often get accumulated inside the inner ear causing pressure and swelling of the delicate ear lining and sometimes symptoms of the hearing loss.
 Inner Ear Damage And Its Impact On Hearing Audicus
Inner Ear Damage And Its Impact On Hearing Audicus
Vestibular neuritis and labyrinthitis are disorders resulting from an infection that inflames the inner ear or the nerves connecting the inner ear to the brain.

Inner ear nerve damage. Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common type of hearing loss. Auditory neuropathy occurs due to damage of auditory nerve which is unable to send the signals from ear to brain. Common symptoms are sudden vertigo nausea vomiting and walking with difficulty.
A portable receiver and headset that intensifies sound without the requirement for wiring. This is a viral infection a cold flu measles chicken pox etc that can temporarily impair or even damage the nerve cells that send sound and balance info from the inner ear to the brain. What may start as a simple clogged ear case may lead to more serious consequences.
If the finding discovered in rats is. Treatments for ear nerve damage include hearing aids. Recently doctors have started injecting steroids directly into the middle ear a procedure called intratympanic treatment.
Ototoxicity ear poisoning is due to exposure to drugs or chemicals that damage the inner ear or the vestibulo-cochlear nerve which sends balance and hearing information from the inner ear to the brain. Vertigo dizziness and difficulties with balance vision or. Medications and surgery although they can be used as treatments are less effective for ear nerve damage than for other types of ear damage.
Inner ear problems such as poor circulation in the ear Calcium debris in your semicircular canals Problems rooted in your brain such as traumatic brain injury What are the symptoms of vestibular balance disorders. If there is nerve damage in the ear the nerves connecting the ear to the brain and in the hearing center in the brain will they repair themselves. It is used for people who had hearing loss due to auditory nerve damage.
An individual with ear nerve damage and hearing loss has limited treatment options. Damage to your auditory nerve or the structures of your inner ear can lead to SNHL. Excessive and persistent noise damages the nerve endings present in the inner ear which can lead to permanent hearing loss.
This type of hearing loss leads to problems converting sound vibrations to neural signals that the brain can. This technique is thought to deliver more of the drug to the ear and to avoid some of the side effects that can come along with oral steroids. Cochlear implants and auditory training according to the University of California San Francisco Medical Center.
Many chemicals have ototoxic potential. The side effects of oral therapy can be mild like weight gain mood changes. Nerve damage in the ear can also cause tinnitus which is a condition where the patient feels persistent ringing in the ears.
Ototoxicity can result in temporary or permanent disturbances of hearing balance or both. Its permanent loss caused by damage to your auditory nerve or the cilia which are tiny hairlike cells in your inner ear. Some nerve cells in the inner ear can signal tissue damage in a way similar to pain-sensing nerve cells in the body according to new research.
This inflammation disrupts the transmission of sensory information from the ear to the brain.
 Am I Losing My Hearing Dr Geissler S Hearing Center
Am I Losing My Hearing Dr Geissler S Hearing Center
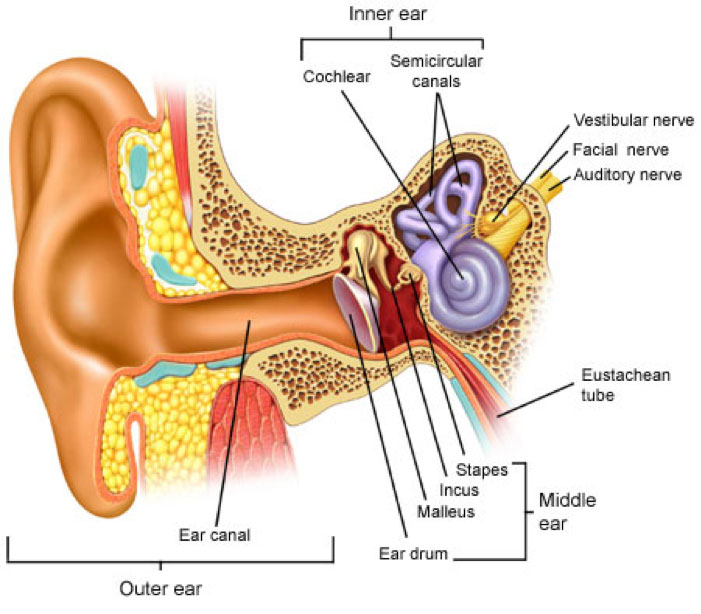 Ear Balance Disorder Treatment Infection Hearing Loss Treatment In Ca
Ear Balance Disorder Treatment Infection Hearing Loss Treatment In Ca
 Neuritis Learn The Different Types And Treatment Options
Neuritis Learn The Different Types And Treatment Options
Vestibular Neuritis Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment
 Vestibular Neuritis National Dizzy Balance Center
Vestibular Neuritis National Dizzy Balance Center
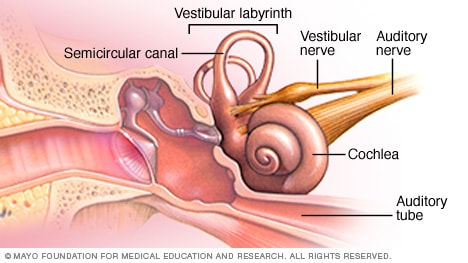 Hearing Loss Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
Hearing Loss Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
 Labyrinthitis Causes Symptoms Treatment And Recovery
Labyrinthitis Causes Symptoms Treatment And Recovery
 Hearing Loss Study At Usc Harvard Shows Hope For Millions
Hearing Loss Study At Usc Harvard Shows Hope For Millions
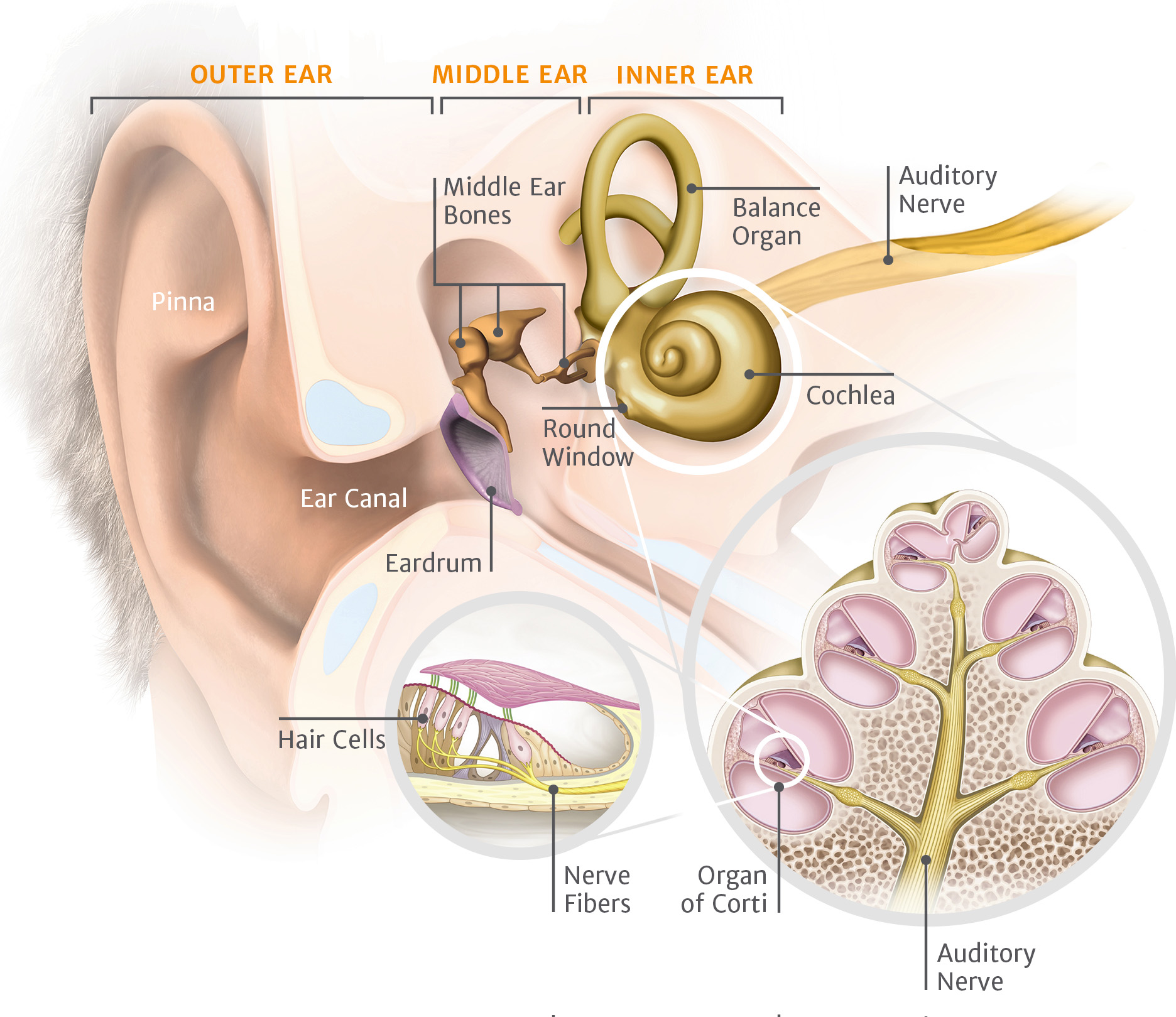
 What Is Inner Ear Nerve Damage Know Its Symptoms Causes Treatment
What Is Inner Ear Nerve Damage Know Its Symptoms Causes Treatment
 Vestibular Nerve Injury Why It Could Be Important To Your Tbi Case Medivisuals
Vestibular Nerve Injury Why It Could Be Important To Your Tbi Case Medivisuals
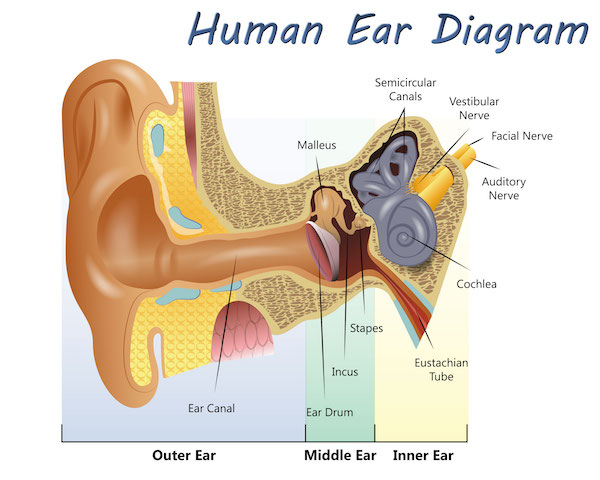
 Vestibular Neuritis And Labyrinthitis
Vestibular Neuritis And Labyrinthitis
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.